I am preparing the EIT Exam for 2017
Also planning to share my notes, Experiences, and Thoughts through this blog
Please review related blogs.
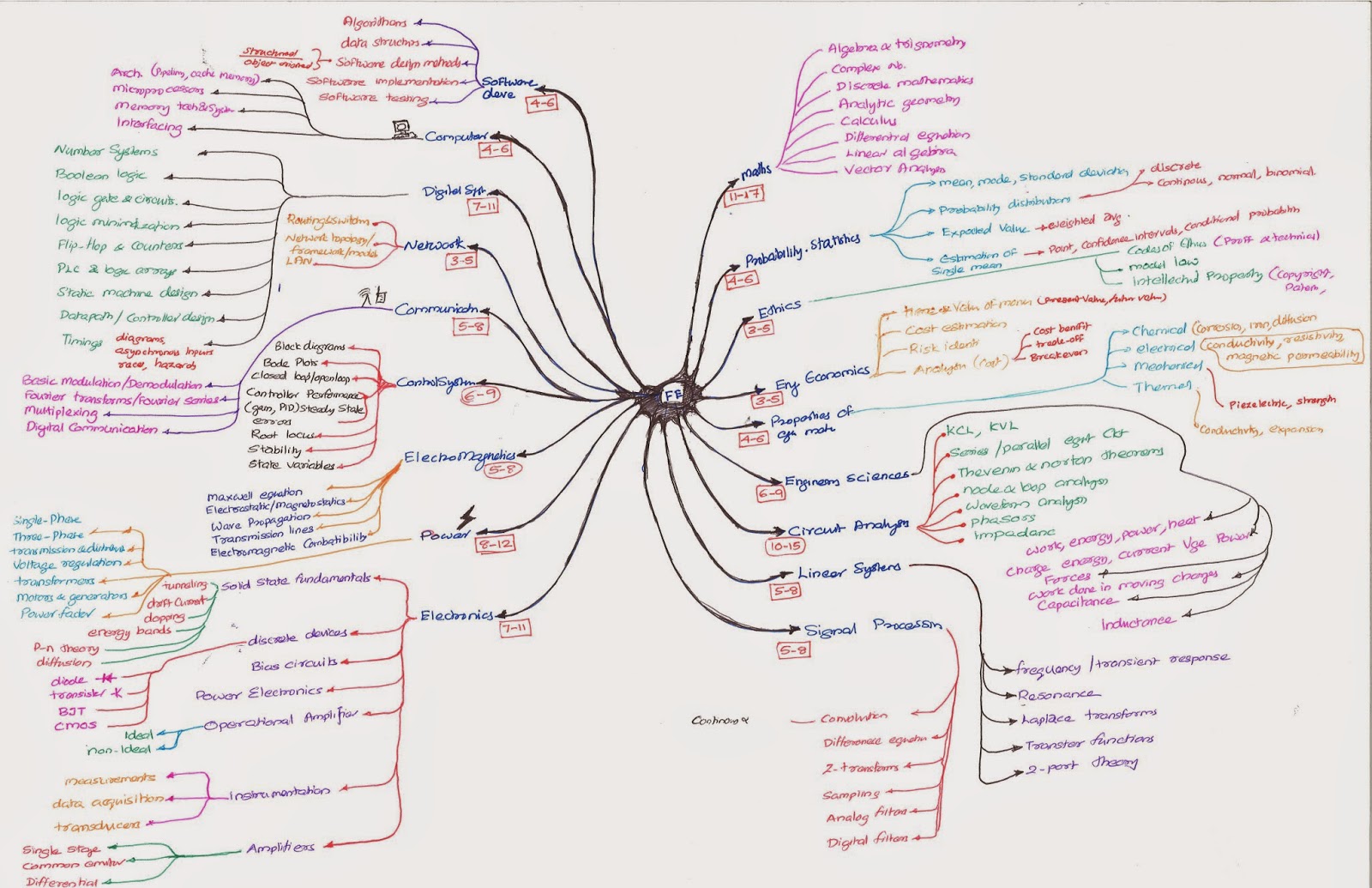
I prepared a mindmap for my exam preparation
My Mind map notes and other handwritten notes will be uploaded in these notes
The FE exam- 110-questions.
The exam appointment time is 6 hours long and includes
need 20 Hour for checking and revision
remaining 5 Hours
5 Hours x 60 Minutes = 300 Minutes
Means 2.72Min for each Q ans A
If we took 2Min for normal Question then 220Min (3Hours, 40 Min) rest of the time for Revision
MY Test Center
Analysis of Marks
1. Mathematics 11–17
A. Algebra and trigonometry
B. Complex numbers
C. Discrete mathematics
D. Analytic geometry
E. Calculus
F. Differential equations
G. Linear algebra
H. Vector analysis
2. Probability and Statistics 4–6
A. Measures of central tendencies and dispersions
mean,
mode,
standard deviation
B. Probability distributions
discrete,
continuous,
normal,
binomial
C. Expected value (weighted average) in decision making
D. Estimation for a single mean
point,
confidence intervals,
conditional probability
3. Ethics and Professional Practice 3–5
A. Codes of ethics (professional and technical societies)
B. NCEES Model Law and Model Rules
C. Intellectual property
copyright
trade secrets
patents
4. Engineering Economics 3–5
A. Time value of money
present value
future value
annuities
B. Cost estimation
C. Risk identification
D. Analysis
cost-benefit
trade-off
breakeven
5. Properties of Electrical Materials 4–6
A. Chemical
corrosion
ions
diffusion
B. Electrical
conductivity,
resistivity
permittivity
magnetic
permeability
C. Mechanical
piezoelectric,
strength
D. Thermal
conductivity,
expansion
6. Engineering Sciences 6–9
A. Work, energy, power, heat
B. Charge, energy, current, voltage, power
C. Forces
between charges,
on conductors
D. Work done in moving a charge in an electric field (relationship between voltage and work)
E. Capacitance
F. Inductance
7. Circuit Analysis (DC and AC Steady State) 10–15
A. KCL, KVL
B. Series/parallel equivalent circuits
C. Thevenin and Norton theorems
Thevenin's theorems lecture explained
Norton theorems
D. Node and loop analysis
E. Waveform analysis
RMS
average
frequency
phase
wavelength
F. Phasors
G. Impedance
8. Linear Systems 5–8
A. Frequency/transient response
B. Resonance
C. Laplace transforms
Class link
D. Transfer functions
E. 2-port theory
9. Signal Processing 5–8
A. Convolution (continuous and discrete)
B. Difference equations
C. Z-transforms
D. Sampling
(e.g., aliasing, Nyquist theorem)
E. Analog filters
F. Digital filters
10. Electronics 7–11
A. Solid-state fundamentals
tunneling,
diffusion/drift current
energy bands
doping bands
p-n theory
B. Discrete devices and models and their performance
diodes,
transistors,
BJT,
CMOS
C. Bias circuits
D. Amplifiers
single-stage/common emitter
differential
E. Operational amplifiers
ideal,
non-ideal
F. Instrumentation
measurements,
data acquisition
transducers
G. Power electronics
11. Power 8–12
A. Single phase and three phase
B. Transmission and distribution
C. Voltage regulation
D. Transformers
E. Motors and generators
F. Power factor (pf)3
12. Electromagnetics 5–8
A. Maxwell equations
B. Electrostatics/magnetostatics
measurement of spatial relationships
vector analysis
C. Wave propagation
D. Transmission lines (high frequency)
E. Electromagnetic compatibility
13. Control Systems 6–9
A. Block diagrams
feed-forward
feedback
B. Bode plots
C. Closed-loop and open-loop response
D. Controller performance (gain, PID), steady-state errors
E. Root locus
F. Stability
G. State variables
14. Communications 5–8
A. Basic modulation/demodulation concepts
AM,
FM,
PCM
B. Fourier transforms/Fourier series
C. Multiplexing
time division,
frequency division
D. Digital communications
15. Computer Networks 3–5
A. Routing and switching
B. Network topologies/frameworks/models
C. Local area networks
16. Digital Systems 7–11
A. Number systems
B. Boolean logic
http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/digital/chpt-7/demorgans-theorems/
C. Logic gates and circuits
D. Logic minimization
SOP
POS
Karnaugh maps
E. Flip-flops and counters
F. Programmable logic devices and gate arrays
G. State machine design
H. Data path/controller design
I. Timing
diagrams,
asynchronous inputs,
races,
hazards
17. Computer Systems 4–6
A. Architecture
pipelining,
cache memory
B. Microprocessors
C. Memory technology and systems
D. Interfacing
18. Software Development 4–6
A. Algorithms
B. Data structures
C. Software design methods
structured
object-oriented
D. Software implementation
procedural
scripting languages
E. Software testing
Also planning to share my notes, Experiences, and Thoughts through this blog
Please review related blogs.
I prepared a mindmap for my exam preparation
My Mind map notes and other handwritten notes will be uploaded in these notes
The FE exam- 110-questions.
The exam appointment time is 6 hours long and includes
- Nondisclosure agreement (2 minutes)
- Tutorial (8 minutes)
- Exam (5 hours and 20 minutes)
- Scheduled break (25 minutes)
need 20 Hour for checking and revision
remaining 5 Hours
5 Hours x 60 Minutes = 300 Minutes
Means 2.72Min for each Q ans A
If we took 2Min for normal Question then 220Min (3Hours, 40 Min) rest of the time for Revision
MY Test Center
Pearson Professional Centers-Gardena (LA) CA
1515 West 190th Street, Suite 405
South Bay Centre, Gardena, California 90248
Phone: 310-532-7521
South Bay Centre, Gardena, California 90248
Phone: 310-532-7521
Analysis of Marks
1. Mathematics 11–17
A. Algebra and trigonometry
B. Complex numbers
C. Discrete mathematics
D. Analytic geometry
E. Calculus
F. Differential equations
G. Linear algebra
H. Vector analysis
2. Probability and Statistics 4–6
A. Measures of central tendencies and dispersions
mean,
mode,
standard deviation
B. Probability distributions
discrete,
continuous,
normal,
binomial
C. Expected value (weighted average) in decision making
D. Estimation for a single mean
point,
confidence intervals,
conditional probability
3. Ethics and Professional Practice 3–5
A. Codes of ethics (professional and technical societies)
B. NCEES Model Law and Model Rules
C. Intellectual property
copyright
trade secrets
patents
4. Engineering Economics 3–5
A. Time value of money
present value
future value
annuities
B. Cost estimation
C. Risk identification
D. Analysis
cost-benefit
trade-off
breakeven
5. Properties of Electrical Materials 4–6
A. Chemical
corrosion
ions
diffusion
B. Electrical
conductivity,
resistivity
permittivity
magnetic
permeability
C. Mechanical
piezoelectric,
strength
D. Thermal
conductivity,
expansion
6. Engineering Sciences 6–9
A. Work, energy, power, heat
B. Charge, energy, current, voltage, power
C. Forces
between charges,
on conductors
D. Work done in moving a charge in an electric field (relationship between voltage and work)
E. Capacitance
F. Inductance
7. Circuit Analysis (DC and AC Steady State) 10–15
A. KCL, KVL
B. Series/parallel equivalent circuits
C. Thevenin and Norton theorems
Thevenin's theorems lecture explained
Norton theorems
D. Node and loop analysis
E. Waveform analysis
RMS
average
frequency
phase
wavelength
F. Phasors
G. Impedance
8. Linear Systems 5–8
A. Frequency/transient response
B. Resonance
C. Laplace transforms
Class link
D. Transfer functions
E. 2-port theory
9. Signal Processing 5–8
A. Convolution (continuous and discrete)
B. Difference equations
C. Z-transforms
D. Sampling
(e.g., aliasing, Nyquist theorem)
E. Analog filters
F. Digital filters
10. Electronics 7–11
A. Solid-state fundamentals
tunneling,
diffusion/drift current
energy bands
doping bands
p-n theory
B. Discrete devices and models and their performance
diodes,
transistors,
BJT,
CMOS
C. Bias circuits
D. Amplifiers
single-stage/common emitter
differential
E. Operational amplifiers
ideal,
non-ideal
F. Instrumentation
measurements,
data acquisition
transducers
G. Power electronics
11. Power 8–12
A. Single phase and three phase
B. Transmission and distribution
C. Voltage regulation
D. Transformers
E. Motors and generators
F. Power factor (pf)3
12. Electromagnetics 5–8
A. Maxwell equations
B. Electrostatics/magnetostatics
measurement of spatial relationships
vector analysis
C. Wave propagation
D. Transmission lines (high frequency)
E. Electromagnetic compatibility
13. Control Systems 6–9
A. Block diagrams
feed-forward
feedback
B. Bode plots
C. Closed-loop and open-loop response
D. Controller performance (gain, PID), steady-state errors
E. Root locus
F. Stability
G. State variables
14. Communications 5–8
A. Basic modulation/demodulation concepts
AM,
FM,
PCM
B. Fourier transforms/Fourier series
C. Multiplexing
time division,
frequency division
D. Digital communications
15. Computer Networks 3–5
A. Routing and switching
B. Network topologies/frameworks/models
C. Local area networks
16. Digital Systems 7–11
A. Number systems
B. Boolean logic
http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/digital/chpt-7/demorgans-theorems/
C. Logic gates and circuits
D. Logic minimization
SOP
POS
Karnaugh maps
E. Flip-flops and counters
F. Programmable logic devices and gate arrays
G. State machine design
H. Data path/controller design
I. Timing
diagrams,
asynchronous inputs,
races,
hazards
17. Computer Systems 4–6
A. Architecture
pipelining,
cache memory
B. Microprocessors
C. Memory technology and systems
D. Interfacing
18. Software Development 4–6
A. Algorithms
B. Data structures
C. Software design methods
structured
object-oriented
D. Software implementation
procedural
scripting languages
E. Software testing